oxd 4.1 Documentation#
Attention
Questions and feedback on oxd 4.1 can be directed to Gluu support. View known issues.
Introduction#
oxd exposes simple, static APIs web application developers can use to implement user authentication and authorization against an OAuth 2.0 authorization server like Gluu.
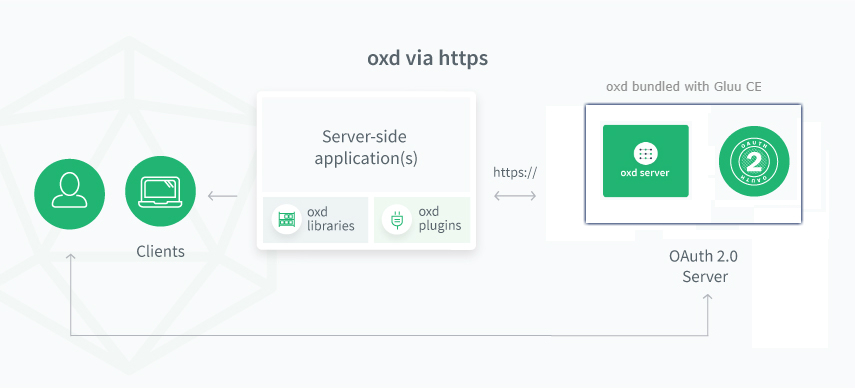
Architecture#
Starting with version 4.1, oxd is offered as one of the several components of the Gluu Server CE. To include oxd in CE instance, just ensure to hit Y when prompted at installation time. The oxd Linux package includes the oxd-server which is a simple REST application. oxd-server is designed to work over the web (via https), making it possible for many apps across many servers to leverage a central oxd service for OAuth 2.0 security.
oxd saves data in own persistence (h2, redis) and acts as RP for OP. Therefore if client is created by oxd on OP side it is highly recommended to update client's data via oxd API. Otherwise if change client's data by configuring OP directly then data in oxd persistence can be outdated which can lead to confusion and unexpected behavior.
Tutorial#
Follow one of our tutorials to learn how oxd works:
Get Started#
To get started:
-
Install Gluu CE and ensure to hit Y when
Install Oxd?is prompted while running setup scripts. -
Configure the
oxd-server -
Restart oxd server using below command.
Ubuntu 16.04 (xenial)
Operation Command Restart oxd server /etc/init.d/oxd-server restartUbuntu 18.04 (bionic)/Debian 9 (stretch)/CentOS 7/RHEL 7
Operation Command Restart oxd server systemctl restart oxd-server -
After Gluu CE server installation is completed wait for about 10 minutes in total for the server to restart and finalize its configuration. After that period, to access Gluu CE server, sign in via a web browser to
hostnameprovided during installation. For quick check whether oxd-server is alive use oxdHealth Checkendpointhttps://$HOSTNAME:8443/health-check. This should return{"status":"running"}ensuring the successful installation of oxd.
Call the oxd API to implement authentication and authorization against an external Authorization Server.
API#
oxd implements the OpenID Connect and UMA 2.0 profiles of OAuth 2.0.
Before using oxd API you will need to obtain an access token to secure the interaction with oxd-server. You can follow the two steps below.
- Register site (returns
client_idandclient_secret. Make sure theuma_protectionscope is present in the request andgrant_typehasclient_credentialsvalue. Ifadd_client_credentials_grant_type_automatically_during_client_registrationfield in/opt/oxd-server/conf/oxd-server.ymlis set totruethenclient_credentialsgrant type will be automatically added to clients registered using oxd server.) - Get client token (pass
client_idandclient_secretto obtainaccess_token. Note ifgrant_typedoes not haveclient_credentialsvalue you will get error to check AS logs.)
Pass the obtained access token in Authorization: Bearer <access_token> header in all future calls to the oxd-server.
OpenID Connect Authentication#
OpenID Connect is a simple identity layer on top of OAuth 2.0.
Technically OpenID Connect is not an authentication protocol--it enables a person to authorize the release of personal information from an "identity provider" to a separate application. In the process of authorizing the release of information, the person is authenticated (if no previous session exists).
Authentication Flow#
oxd supports the OpenID Connect Hybrid Flow and Authorization Code Flow for authentication.
Learn more about authentication flows in the OpenID Connect spec.
oxd Authorization Code Flow#
You can think of the Authorization Code Flow as a three-step process:
- Redirect a person to the authorization URL and obtain a code /get-authorization-url
- Use the code to obtain tokens (access_token, id_token and refresh_token) /get-tokens-id-access-by-code
- Use the access token to obtain user claims /get-user-info
UMA 2 Authorization#
UMA 2 is a profile of OAuth 2.0 that defines RESTful, JSON-based, standardized flows and constructs for coordinating the protection of APIs and web resources.
Using oxd, your application can delegate access management decisions, like who can access which resources, from what devices, to a central UMA Authorization Server (AS) like the Gluu AS.
Native Libraries#
oxd APIs are swaggerized! Use the Swagger Code Generator to generate native libraries for your programming language of choice.
For more information about generating native clients, check our FAQ.
Compatibility#
oxd 4.1 has been tested against the following OAuth 2.0 Authorization Servers:
OpenID Providers (OP)#
UMA Authorization Servers (AS)#
Source code#
The oxd source code is available on GitHub.
License#
oxd 4.1 is available under the AGPL open source license.
Support#
Gluu offers support for oxd on the Gluu Support Portal. In fact, we use oxd and a Gluu Server to provide single sign-on across our oxd portal and support app!
For guaranteed response times, private support, and more, Gluu offers VIP support.