Gluu Radius#
Overview#
The Gluu Server can now be configured to include a RADIUS server based on the TinyRadius Java library. The implementation ("Gluu Radius") supports RADIUS authentication, but does not provide RADIUS accounting support. RADIUS accounting packets are simply ignored.
Note
For a more performant RADIUS solution, try our plugin for Radiator, a robust AAA server built for ISPs and carriers.
Installation#
During installation, while running setup.py, simply select Y when you are asked to install Gluu Radius.
Service#
Gluu Radius runs as a service from within the Linux container. Certain configuration settings will require a service restart. View the Services Commands doc for commands for the OS in use.
Configuration#
With Gluu Radius installed, a sidebar menu item for Radius will appear in oxTrust. The GUI can be used to perform the following operations:
- Configure the running instance of Gluu Radius
- Add/Edit/Remove NAS/Radius clients
In addition, the Gluu Radius config file can be found in the Linux container under: /etc/gluu/conf/radius/gluu-radius.properties
Basic Configuration#
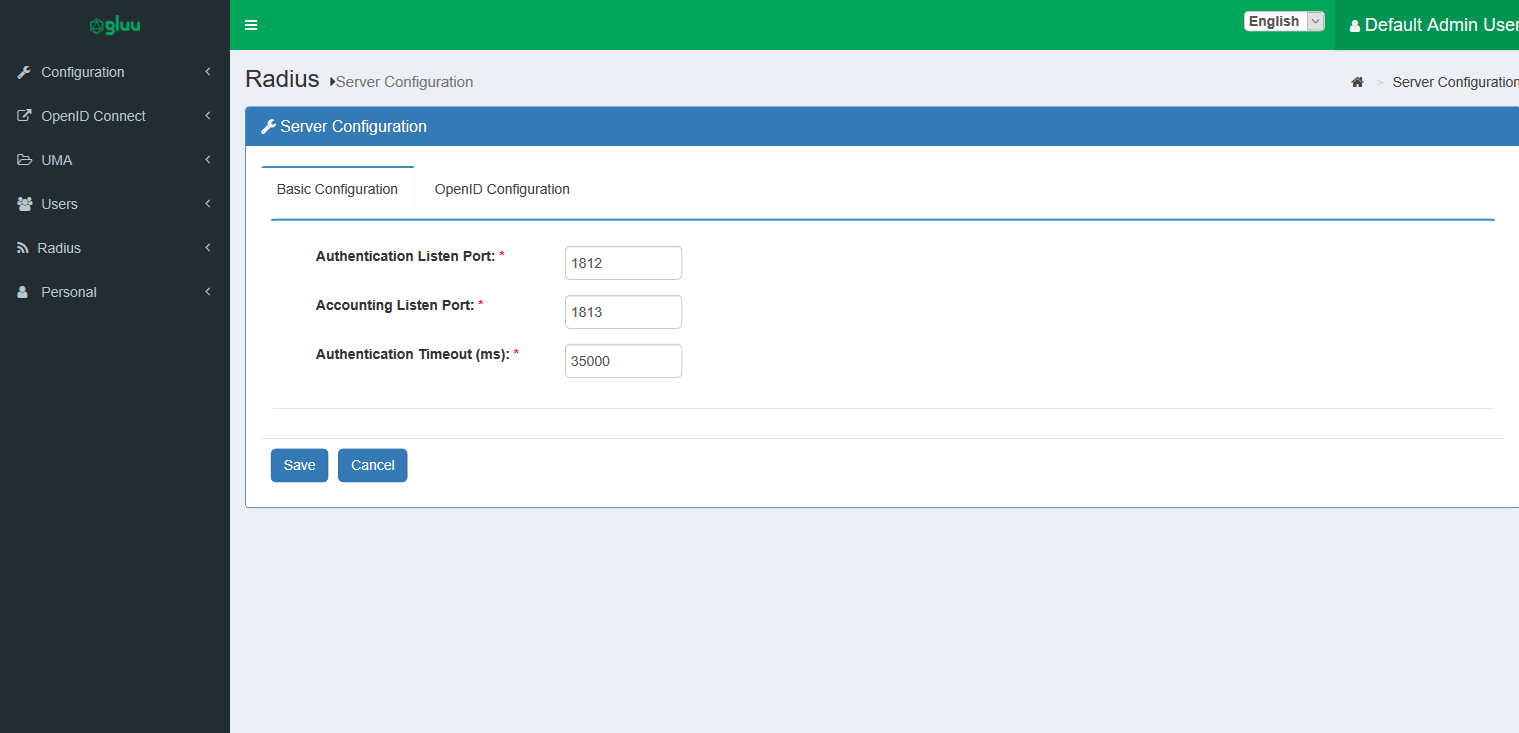
In oxTrust, navigate to Radius > Server Configuration and select the Basic Configuration tab.
The following settings can be configured:
-
Authentication Listen Port: This is the port on which the server listens for authentication requests. -
Accounting Listen Port: This is the port on which the server listens for accounting requests. Currently, the server simply ignores accounting packets. -
Authentication Timeout: This is the maximum amount of time in milliseconds between when an authentication request is initiated and the user approving authentication. This applies only for long lived two-factor authentication based requests (e.g. Super-Gluu).
Note
Any change to any of these configuration parameters will require a restart of the gluu-radius service. Make sure the ports selected for authentication and accounting are open.
 .
.
OpenID Configuration#
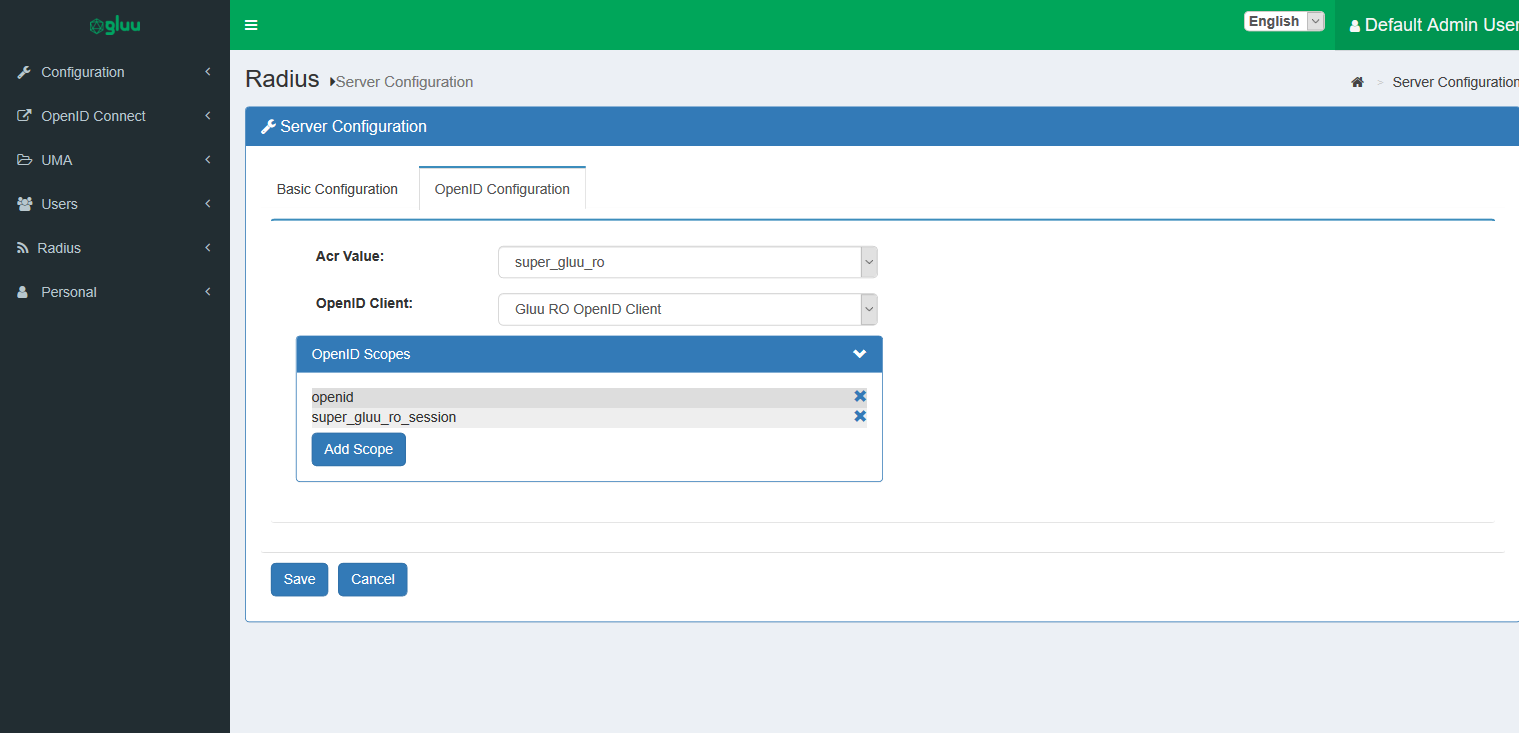
In oxTrust, navigate to Radius > Server Configuration and select the OpenID Configuration tab. Configure the following:
-
Acr Value: Gluu Radius relies on a custom script of typeResource Owner Password Credentials. Select another script of the same type that can be used for authentication within certain constraints which will be given later. -
OpenID Client: Gluu Radius relies on an OpenID client for authentication. You may specify another client here, but this is also possible within certain constraints which will be given later. -
OpenID Scopes: These are the scopes used during the password grant token request. For proper operation, the scope list must contain theopenidscope.
Note
A change to any of these configuration parameters will require a restart of the gluu-radius service.
Radius Clients#
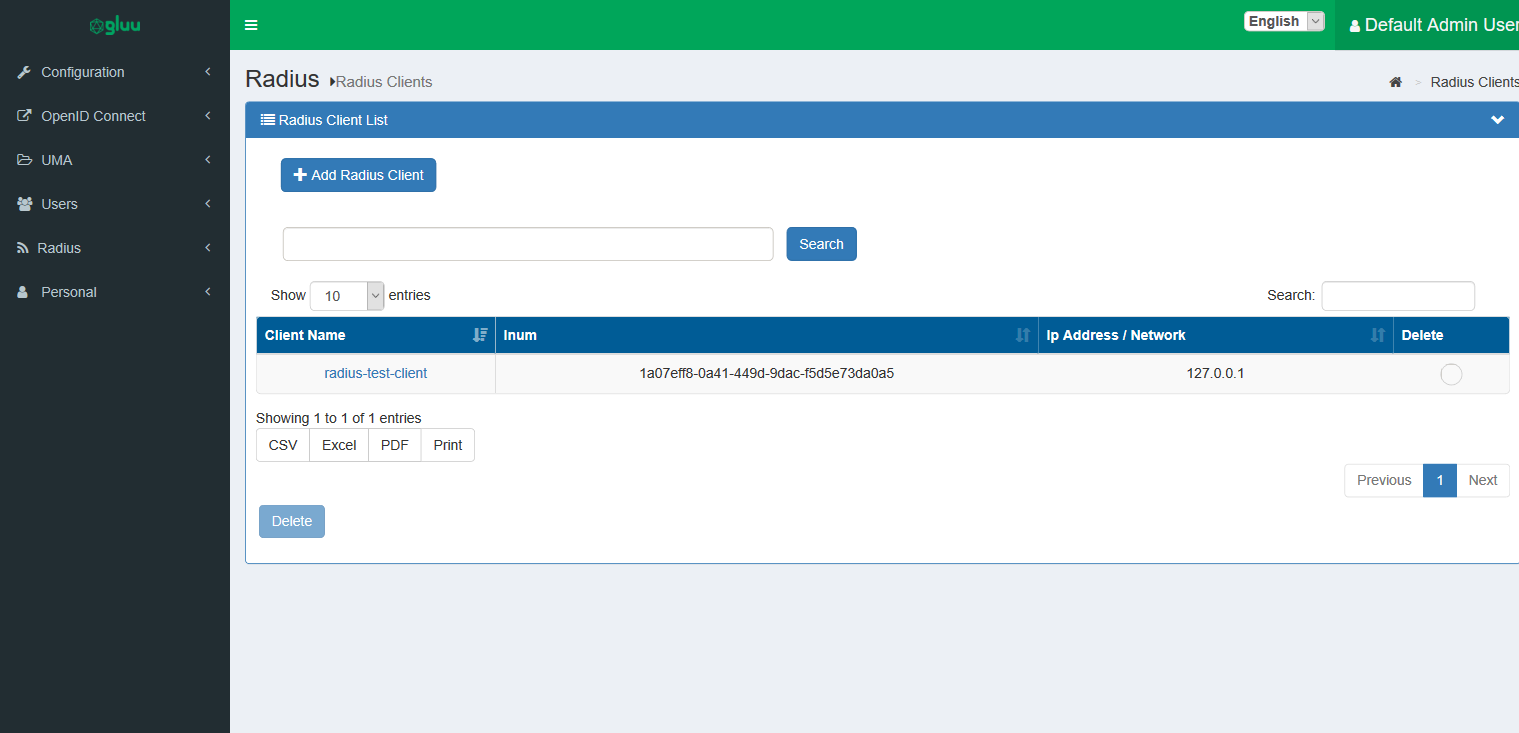
From the oxTrust UI , go to Radius > Radius Clients. A list of Radius / Nas Clients will appear which are authorized to authenticate via the Radius server.
-
To add a new Radius Client, click
Add Radius Client. -
To edit an existing client's details, click an existing client's name.
-
To delete multiple clients at the same time, bulk select one or more Radius clients and click
Delete.
Adding/Updating A Radius Client#
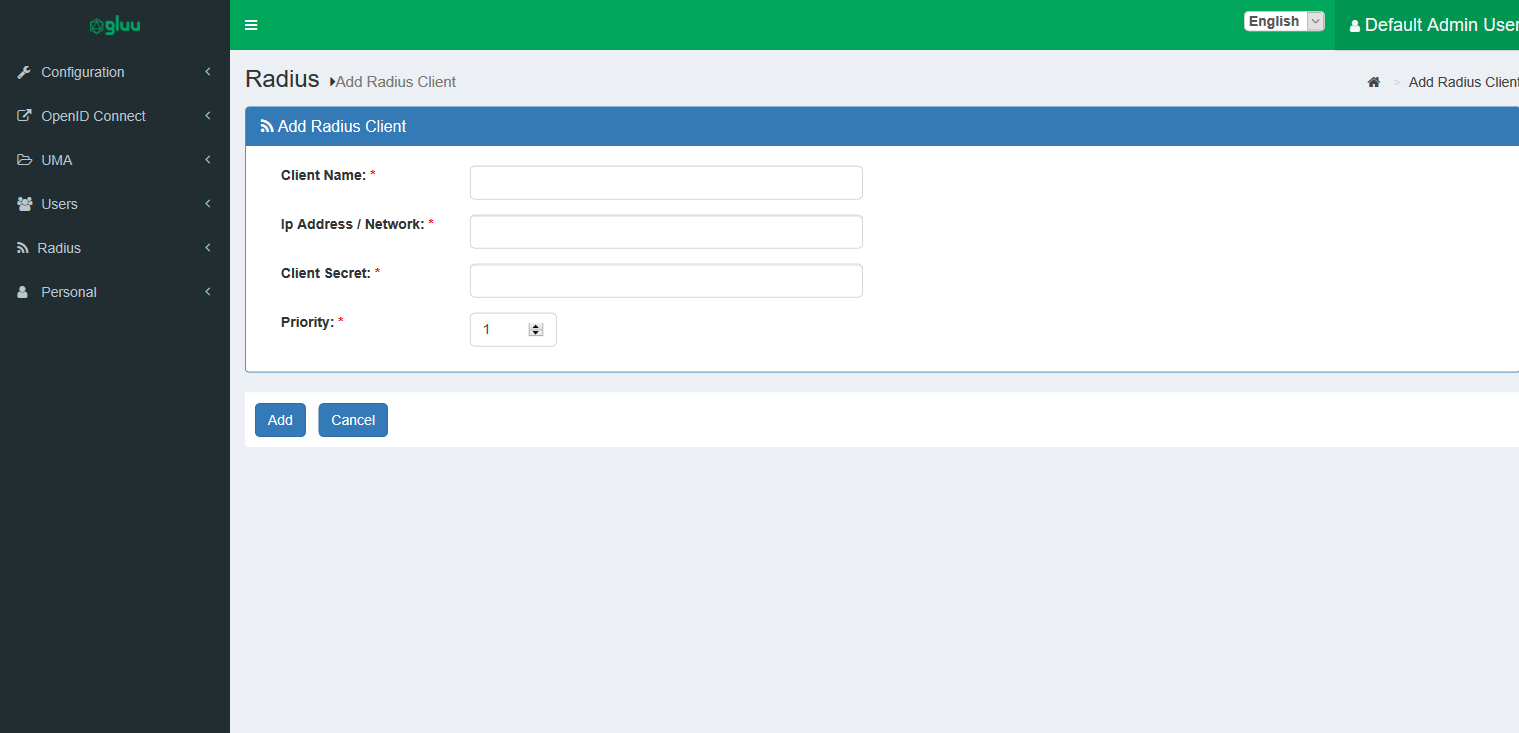
From the oxTrust UI, go to 'Radius > Radius Clients' , then click on Add Radius Client and specify the following:
-
Client Name: An easy mnemonic to recognize the client. -
Ip Address/Network: Specify either an IPv4 address here (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) or a CIDR subnet (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xxx). The CIDR notation will match all Radius/NAS clients originating from that network. -
Client Secret: The Radius Client's secret. -
Priority: Radius clients are matched by the gluu-radius not only by IP Address/Network but also by priority. So, if two entries may match for one client (Ip Address/Network), the entry with the highest priority will be selected.
Advanced Topics#
This section covers optional advanced configuration topics.
Gluu Radius config file#
The Gluu Radius configuration file can be found under /etc/gluu/conf/radius/gluu-radius.properties
in the linux container. There are a couple things you can change from the configuration file.
Any change to this file will take effect only after restarting the gluu-radius service.
Turning on/off listening.#
It is possible to turn listening on/off for the radius server. This feature is useful when using gluu-radius exclusively for key re-generation.
The configuration key can have two values, true or false
radius.listen.enable = true
Authentication Scheme#
There are two available authentication schemes:
onestep, as its name suggests, is the single step authentication scheme. Enabling it will have the Radius server authenticate the user and return the authentication status immediately.twostep, as its name suggests, is two-step (two factor authentication). This is the default. In its current implementation , it performs two step authentication using super-gluu.
radius.auth.scheme = twostep
Key Re-generation interval#
This configuration parameter controls how often the keys used for authentication are re-generated. The value is in days. A value of 0 disables key re-generation.
# regenerates the keys every day
radius.jwt.keygen.interval = 1
Change JWT authentication algorithm#
By default, the algorithm used by Gluu Radius for authentication is RS512 (RSASSA-PKCS1-v1_5 using SHA-512).
To change the algorithm, follow these steps:
-
In oxTrust, navigate to the configuration settings for the OpenID client used by Gluu Radius (see OpenID Configuration) and tab over to
Encryption/Signing. -
Change the option
JWS alg Algorithm for Authentication Method to Token Endpointto the algorithm of your choice.
Note
The algorithm must be a keypair algorithm.
-
Now, in the JWKS section (or in your jwks if you provided a URL), copy the
kidcorresponding to the algorithm you selected, and change the following line in the Gluu Radius configuration file:radius.jwt.auth.keyId = <kid> -
Once complete, restart the
gluu-radiusservice.
External jwks#
Using an external jwks requires you pasting the contents of the jwks into the JWKS section in the Encryption/Signing tab
of the OpenID client used by gluu-radius for authentication.
You also need to provide a keystore , which contains all of the keys , with each entry name having the corresponding kid
for each JWKS entry. Generation of a keystore file and/or a JWKS is outside the scope of this document.
You will need to change the following in the configuration file.
radius.jwt.keyStoreFile = <location of keystore file>
radius.jwt.auth.keyId = <kid of public key used for authentication>
radius.jwt.auth.keyStorePin = <encrypted pin for the keystore>
/opt/gluu/bin/encode.py to encrypt the plaintext keyStore password.
Custom OpenID client#
There are a few constraints if a custom OpenID client is in use:
- The client must support private key JWT authentication.
- The client must have the
super_gluu_ro_sessionscope or any scope which will add a__session_idclaim containing an authenticated session id to the idtoken forpasswordtoken grant requests. - The client must have the
passwordgrant type - The client must be enabled to include claims in the ID Token.
- The keys used in the jwks for the client need to be saved in a keystore and have
gluu-radiuspoint to them as specified in the section above.
To see an example, review the default OpenID Client that ships with Gluu Radius.
Custom authentication script#
Likewise, there are a few additional constraints if a custom authentication script is in use:
- The script must be of type
Resource Owner Password Credentials - The script must accept and process a
__passwordhttp post parameter containing the user's password and not thepasswordhttp post parameter. - The script must accept and process a
__stephttp post parameter. - When
__stepis equal toinitiate_auth, the custom script must authenticate the user using the provided credentials and must create a session on the server (authenticated or not) and return the session id in the idtoken with a claim name of__session_id. If the user can't be authenticated, the script must return false. - When
__stepis equal toverify_auth, the custom script must get the http post parameter called__session_idand verify if the associated session is authenticated. If it's not authenticated , the script must returnfalse.
To see an example, review the default authentication script that ships with Gluu Radius.