Custom Authentication Script Tutorial#
Overview#
Interception scripts enable you to customize your Gluu authentication service. In an interception script you can call external APIs, like a commercial authentication service, a DDoS protection service, a fraud detection service, etc., to make your authentication process more secure. In addition, interception scripts give you the ability to implement business driven policies during authentication.
For example, you may want to only prompt users in a certain group for two-factor authentication. Or, you may want to only prompt a user for two-factor authentication if the request is coming from an unknown IP address. These types of policies can be incorporated into your authentication service by writing an interception script that uses the methods described below.
This tutorial explains how to write a script to implement a two-step out-of-band authentication using Twilio to send an SMS with a one-time password. At the end of this tutorial you should have a better understanding of how to write your own custom scripts. For reference, you can review the completed Twilio custom authentication script here.
!!! Warning: Be aware that in case default authentication methods for oxTrust and oxAuth are set to "Default" on the "Default Authentication Method" tab of "Manage authentication page", you may lock yourself out of web UI by simply enabling an authentication script. Please check this page for full explanation
Suggested Development Environment#
Gluu Server custom scripts are written in Jython. We recommended using Eclipse for coding purposes.
Custom Script Location#
The GUI for custom authentication scripts can be found by navigating to
Configuration > Manage Custom Scripts > Person Authentication.
Custom scripts can either be inserted directly into the GUI or you can
specify a path to the script. We recommend specifying a path in order to
make development easier. To specify a path, select File from the Script Location Type field in oxTrust and the Script Path input box will be displayed:
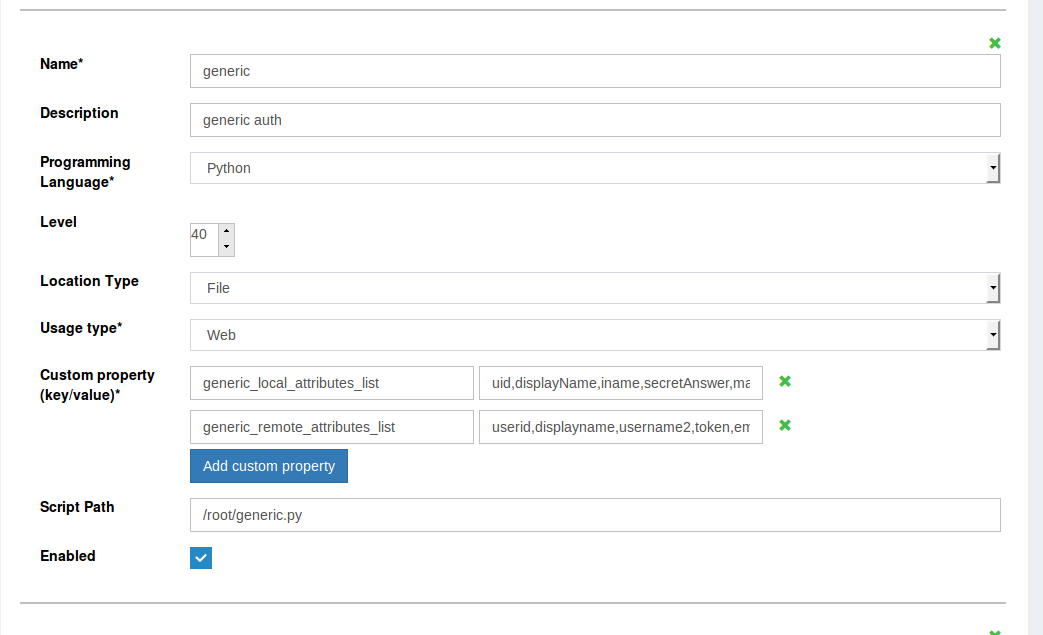
The LDAP option in the Script Location Type can be used to store the script in the LDAP tree once development is complete. Remember that selecting the LDAP method requires the script to be copied in the input box that appears upon LDAP selection:
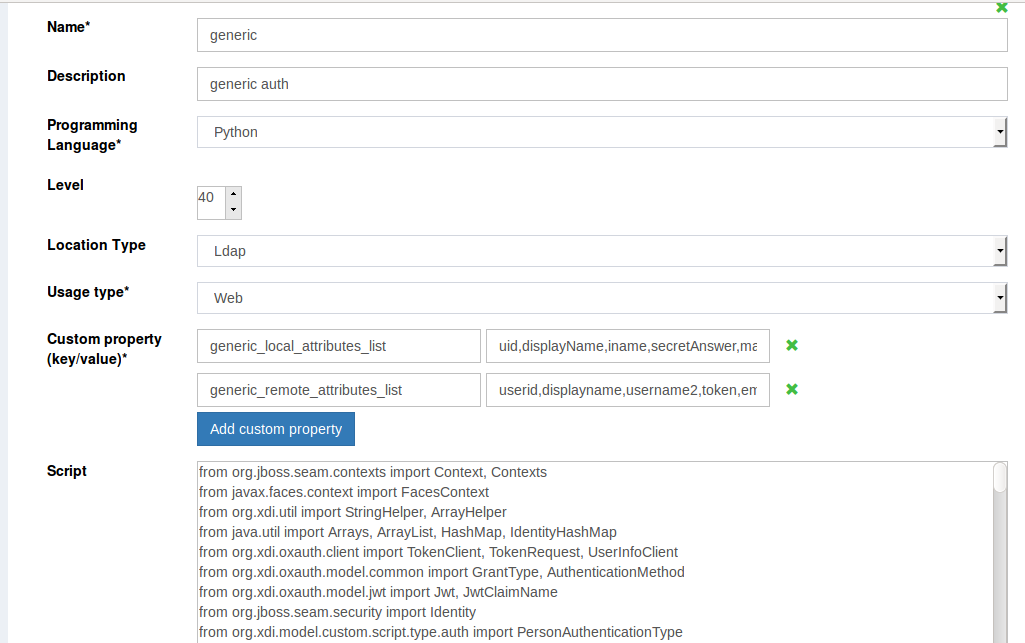
Fields in Custom Script:#
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Script |
| Description | [optional] Description of the script |
| Programming Language | Currently Python is supported, in the future jscript and Java will be added |
| Level | Authentication Level for the authentication, which determines the security level |
| Location Type | The script can be stored in a "File" or in "LDAP" |
| Usage Type | The script can be written for Web, Native or Both types of applications |
| Custome Property | Determines the key and value of the custom property, which can be added to the authentication to pass values between steps |
| Script Box | Script Box will displayed if Location Type is selected as "File", to enter the path of the script |
| Script | Script Box will be displayed when Location Type is selected as "LDAP" |
Create Initial Files#
Create the following files:
- A Python file for your script;
- One or more XHTML files if you have a custom form for your authentication;
- One or more XML files (you'll need one for each XHTML file) that provide information to the web server about how to display the XHTML file.
Samples and Documentation#
There are many good examples of authentication interception scripts in Gluu's oxAuth integrations folder. The respective XHTML and XML files are checked into the auth folder. The interfaces for authentication interception scripts can be found in the Gluu Documentation.
We used the Basic Script
as a template. The Wikid forms
were also used as a template since it requires that we pass the value of the code obtained from Twilio to step 2 of the authentication to validate and authenticate the user.
The Wikid authentication script was also looked upon for examples on how to process the form.
Implement methods - Using Twilio SMS#
Steps to add a custom template and pass values between 2 steps of authentication for our sample Twilio script:
- Login to Gluu UI;
- Navigate to
Configuration>Manage Custom Scripts; - Scroll to the end of the page and click
Add custom script configuration; - Enter the Name, Description, and Programming Language (Python will be by default);
- Select the Level to set a security level;
- Select Location Type for the script;
- Select the Usage Type for the authentication;
- Define Custom property, which in our example is provided by Twilio;
- Click on Enabled to enable the script;
- Scroll down to the bottom of the form and click
submit; - After the custom script is added, navigate to
Configuration>Manage Authenticaion>Default Authentication Methodand change the oxTrust authentication mode to "Twilio" (or the custom name of your script).
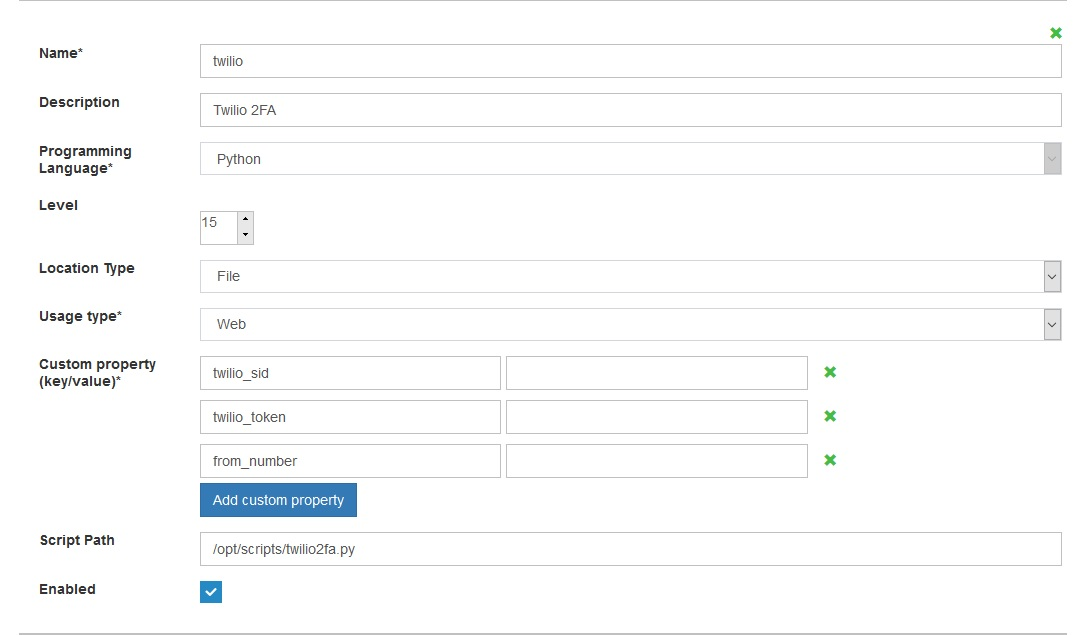
Note: All three below custom properties are mandatory for the Twilio Two-Factor Authentication script to work
- ACCOUNT_SID - Numerical sequence of numbers, to identify the token assigned to the user associated with Twilio.
- AUTH TOKEN - Alphanumerical number provided by Twilio for the account holder to identify the user.
- FROM_NUMBER - Number which is either assigned by Twilio or can be a number user provides to send the code from.
As shown in the below illustration:
Methods#
authenticate():
The most important method to implement is the authenticate method. This is where the main business logic is located for
the authentication workflow. It is possible to switch on the step, with the if (step == 1): statement. In oxAuth, there is no
assumption that step 1 and step 2 happen on the same server, therefore the value is stored in LDAP using a temporarily created attribute that can be retrieved in step 2. The step is sent to the authenticate method, which helps to save and retrieve the values as required.
Below are a few Methods and Libraries used to Save the Value to LDAP and retrieve the values as required:
random.randit()
random.randit("start number",""end number") Generates the code as required.
Example: random.randit(10000,99999)
context.set()
This particular method is obtained from jboss to pass the session attribute value to LDAP by creating a temporary attribute which has a limited lifetime and can be retrieved within the life span, otherwise it expires and the session becomes invalid. Save the value of the code obtained through the code generator method. context.set("Name of the temp attribute", <key>) where <key> is the value that needs to be stored temporarily in ldap.
Example: context.set("code",code)
UserService.instance()
Gets the user login instance
ServerUtil.getFirstValue():
To access information from requestParameters in your script with ServerUtil.getFirstValue(requestParameters, <key>) where <key>
specifies the value you want to retrieve, you can also use another method requestParameters.get("<key>")
where <key> specifies the value you want to retrieve .
userService.getUserByAttribute():
getUserByAttribute("LDAP Attribute", <key>) method accesses information in LDAP and retrieves the value of the attribute comparing the value of the <Key>.
Example: userService.getUserByAttribute("uid", user_name)
getAttribute():
To retrieve the value of an attribute from LDAP, getAttribute("LDAP Attribute name") can be used.
Example: getAttribute("mobile")
requestParameters.get():
requestParameters.get(<key>) can be used to retrieve values passed from the form through the headers. This will retrieve the values from the form via header and can be stored in a string. Where <key> is the value to be retrieved from header.
Example: abc = requestParameters.get("passcode")[0].strip()
getCountAuthenticationSteps():
Another method usually needed to implement is getCountAuthenticationSteps. This method normally just returns 1, 2, or 3. If implementing an adaptive authentication strategy, where the number of steps depends on the context.
Note
Check the Duo script
for a good example of how getCountAuthenticationSteps can be used to implement adaptive authentication. The Duo script is scripted so that two-factor authentication is only presented for users in the IT group. The script checks for group membership and dynamically adjusts the number of steps. This can be implemented to check for any logic or attribute during the authentication, like "country" or "region".
getExtraParametersForStep():
If required to save session variables between steps, use the getExtraParametersForStep method. The Gluu Server persists
these variables in LDAP in able to support stateless, clustered two-step authentications.
getPageForStep():
If required to display a special Web page for an interactive login, or even a custom first page, you'll need to implement the
getPageForStep method to specify the page you want to return for a given step.
session_attributes.get():
The attribute value that are saved by the session using context.set. This method is derived from the oxauth core java libraries and called using the SessionState parameters which is defined in the code or program as session_attributes.get(<key>), where <key> is the session atribute value that is stored in the ldap.
Example: session_attributes.get("code")
Logout():
It can be used in cases when you need to execute logout logic specific to this authentication script (like notifying remote/3rd party services, writting to databases etc) when oxAuth receives an end session request. In contrary to scripts of "Application session managment" type, this function will only be called in case the user who in process of logging out used this very script where it's implemented for initial authentication. Also, it allows oxAuth to stop processing the end session request workflow if it returns False. As a result it should either return True or False
This method is not mandatory. A stub definition of this function is already present in most scripts.
def logout(self, configurationAttributes, requestParameters):
return True
Application session Logout#
Custom scripts of type "Application session" are launched when user's session at oxAuth is about to be killed, mostly to provide opportunity to notify some 3rd party apps or remote services about the fact, perhaps to conduct some cleaning tasks there, or end user's session there too (if those services don't support mechanisms like "Frontchannel logout" etc)
We also must mention that we have a similar feature supported for our Authentication custom scripts. Each of those script may implement logout function like below:
def logout(self, configurationAttributes, requestParameters):
return True
Its purpose mostly the same, beside the fact that each auth script's function will only be called for users whose authentication during login attempt was handled by corresponding script, but scripts of "Application session" type will be called every time during logout of each user, regardless of what method of authentication he used during login.
Saving and Passing Values#
Saving Values:#
context.set can be used to save values of the required key to an attribute temporarily and the created temporary attribute will be alive only for limited time and expires and gets removed, by that way, adding new attribute to the user is not messed up. And also the expired attribute kills the validity of the session and becomes invalid.
Retriving and passing values between steps#
Using session_attribute.get() method, stored session attribute can be retrieved anywhere between the authentication method, enabling values to be passed between multiple authentication methods for verification and validation. Generated code and the entered "code" in the form can be verified using a simple if and the "code" from the form can be obtained using the requestParameters.get() method or serviceUtil.getFirstValue() method.
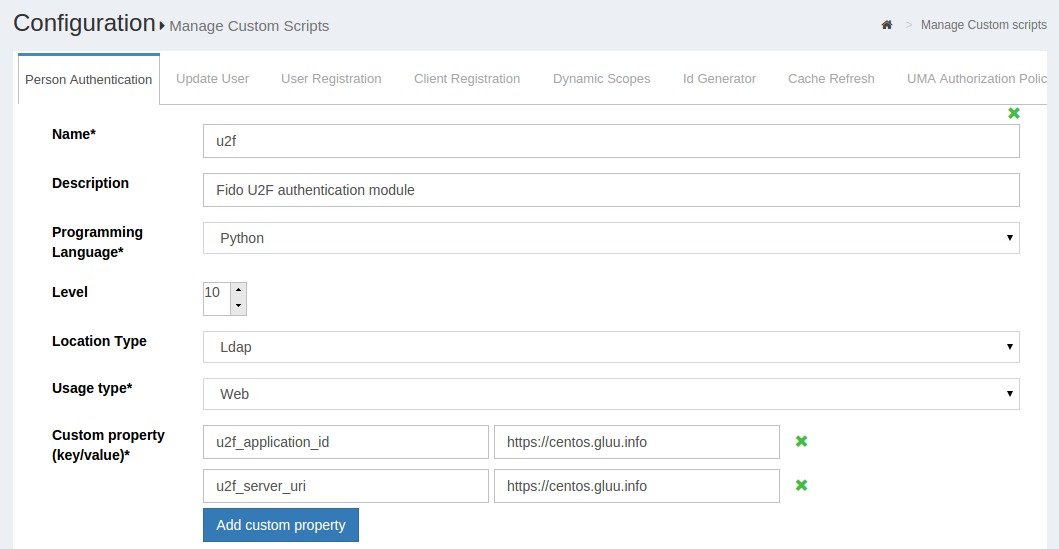
Custom Properties#
Sometimes it is helpful to enable system administrators to enter properties that might frequently change. If administrators are not allowed to modify the script, the Custom Property feature can be used as illustrated in below screenshot:
configurationAttributes.get("<key>").getValue2"():
To access this information in your script with configurationAttributes.get("<key>").getValue2() where <key> specifies the value you want to retrieve.
Returning a message to the user#
It is possible to use the Context to return a message to the user, which could be especially useful if an error occurs or some kind of user action is required.
Adding Libraries#
Pure Python libraries can be added to /opt/gluu/python/libs, and jar files can be added to /opt/gluu/jetty/oxauth/lib/ext.
Note
jar files should be added within chroot.
Testing#
When the scripting is done, you can test the script by printing the statments to oxtrust.log under /opt/gluu/jetty/identity/logs/oxtrust.log.
Prefixing the logs will help to find the script using tail command tail -f | grep <prefix>, the prefix logs will provide the script output while one trys to login using the script.
In the Twilio test script, a specific method called printOut has been scripted to make it easier to add this prefix.
Also, remember that putting all the code in a try / catch is a good practice to avoid unhandled exceptions, since during debugging exceptions may provide a hint at what's causing the issue.
Further logs to debug and monitor the sequence can be done using oxauth_script.log and oxauth.log under /opt/gluu/jetty/identity/logs/ which is within the chroot.
Reverting Authentication Method#
It is not uncommon to get locked out of the Gluu Server while testing the authentication script.
In such case, refer to Reverting Authentication Method to revert back to the older authentication method: